.

Beta-Caryophyllene: Both Terpene & Cannabinoid
Out of 150 terpenes found in cannabis, beta-caryophyllene stands out as one of the most interesting. It lends a spicy and woody flavour to buds and exerts a soothing and relaxing effect. On top of this, it also falls into the category of cannabinoids alongside THC and CBD. Find out everything you need to know below!
Contents:
Have you ever detected spicy, peppery, or woody notes when smoking weed? Well, you have beta-caryophyllene to thank for that pleasant experience. Both a terpene and a cannabinoid, this molecule ranks as one of the most fascinating chemicals in the cannabis plant. Learn everything you need to know about it below.
Introducing Beta-Caryophyllene
Even if you’ve never heard of beta-caryophyllene, chances are you’ve inhaled this molecule more times than you can count. As one of the most dominant terpenes found across all cannabis strains, beta-caryophyllene impacts both the flavour and effects of many different cultivars.
Emerging studies demonstrate its promising therapeutic potential, and research shows it acts simultaneously as a cannabinoid and a terpene.
-
Beta-Caryophyllene as a Dietary Cannabinoid
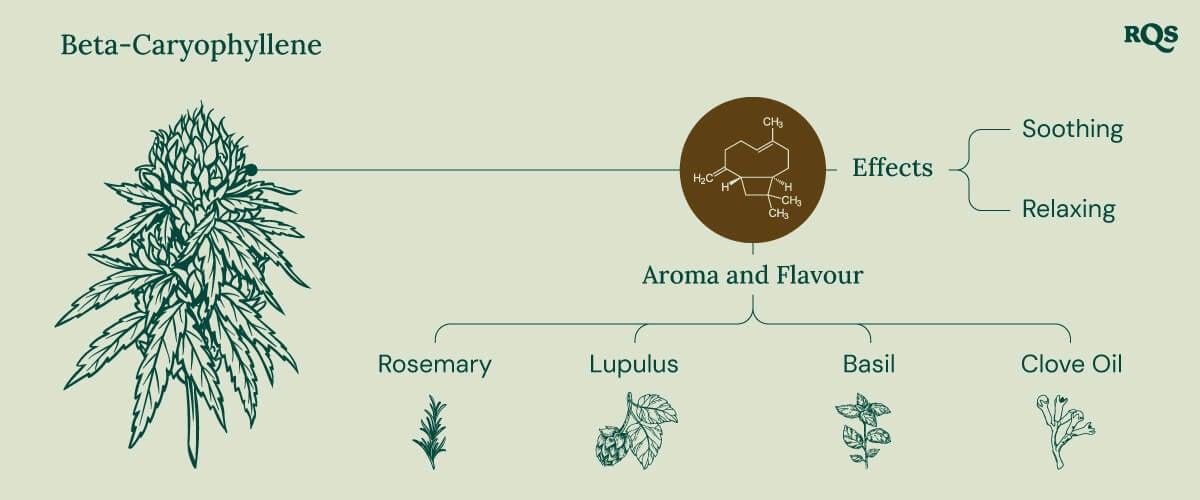
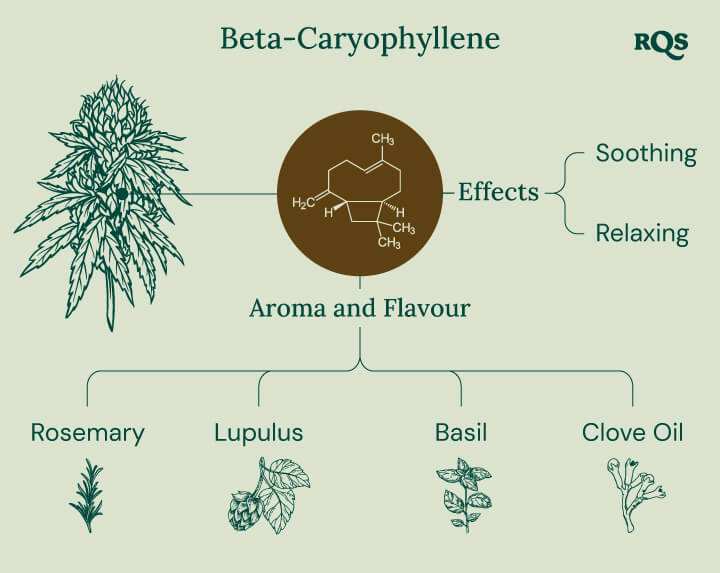
Way back in 2009, researcher Jürg Gertsch and colleagues published a paper[1] titled “Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid”. The findings presented in this publication set beta-caryophyllene aside from many other terpenes by placing it in the chemical category of cannabinoids—alongside THC and CBD. By directly binding to the CB2 receptor of the endocannabinoid system, a body-wide network tasked with maintaining biological balance, beta-caryophyllene can potentially impact the immune system, liver, bones, heart, and brain. The “dietary” component of this molecule’s title stems from the fact that most of us ingest beta-caryophyllene on a routine basis owing to its presence in common herbs and spices such as rosemary, cloves, black pepper, oregano, basil, and cinnamon.


The Chemistry of Beta-Caryophyllene
If you know anything about terpenes, you’ll understand that large structural differences set many of these molecules apart. All of them are based on isoprene units—five-carbon molecules that form the building blocks of different terpenes. Small monoterpenes such as pinene and myrcene are composed of two isoprene units, meaning they possess a total of 10 carbon atoms. In contrast, beta-caryophyllene belongs to a group called sesquiterpenes that possess three isoprene units and a total of 15 carbon atoms.
As a bicyclic sesquiterpene, beta-caryophyllene has a unique molecular structure that features two ring systems. The first nine-membered ring forms the backbone of the molecule. The second four-membered ring, a relatively rare cyclobutane ring, fuses to the larger backbone and gives the molecule the unique structure that allows it to work as both a terpene and a cannabinoid.
-
Aromas and Flavour of Beta-Caryophyllene
While beta-caryophyllene occurs in most cannabis strains, some varieties possess much higher concentrations of the terpene. Caryophyllene in cannabis provides a warm and spicy aroma with notes of sweetness and wood. The flavour of these buds is clove-like, with hints of spice and pepper. This cannabis terpene is present in plenty of plants, such as:
- Rosemary
- Lupulus
- Basil
- Clove oil
-
Effects Associated with Beta-Caryophyllene in Cannabis
The caryophyllene terpene not only contributes to the flavours and aromas of certain strains, but it directly impacts their effects. Users subjectively describe beta-caryophyllene effects as soothing and relaxing.
Beta-Caryophyllene: A Look at the Research
Cannabis science remains in the early stages, and very few human trials exist that demonstrate the effectiveness of specific cannabinoids and terpenes in humans. However, the research surrounding beta-caryophyllene is indeed progressing. While we can’t make any solid conclusions on its therapeutic effects, it’s interesting to see what researchers have discovered so far. Find out more below.
-
The Entourage Effect
The entourage effect posits that certain cannabis constituents are more effective when administered together compared to when given in isolation. Based on this thinking, many cannabis users prefer full-spectrum extracts and whole flowers because of the wealth of phytochemicals they contain. A 2024 cell study[2] conducted at the University of Florence, Italy, found that a combination of beta-caryophyllene and CBD demonstrated superior anti-inflammatory effects than either molecule administered separately.
-
Chronic Pain
An increasing amount of studies are testing cannabis phytochemicals on cell and animal models of pain. A 2023 study[3] conducted at the University of Arizona administered several terpenes in a mouse model of neuropathic pain, including beta-caryophyllene. The researchers concluded, “Overall, our observations support the translational utility of terpenes as potential treatments for neuropathic pain..”.
-
Fatty Liver Disease
The most common cause of chronic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), affects around 32%[4] of the world’s adult population. While no specific medication is used to treat the condition, some researchers are focusing on terpenes as a therapeutic aid. After applying beta-caryophyllene to a cell model of the disease, researchers from the University of Turin, Italy, concluded[5]: “Taken together, our results suggest that BCP [beta-caryophyllene] is a promising molecule for the treatment of NAFLD.”
-
Addiction
Beta-caryophyllene effects also show promise in the future of addiction treatment. Animal studies have tested the terpene in addiction models against drugs such as cocaine, nicotine, alcohol, and methamphetamine. The authors of a review[6] regarding the effects of the molecule on drug addiction concluded: “Preclinical studies have reported promising results with BCP in animal models of substance disorders. Further research, including studies in humans, are warranted to establish its therapeutic potential and its mechanisms of action.”
Beta-Caryophyllene: A Fascinating Cannabis Phytochemical
Beta-caryophyllene stands as one of the most unique phytochemicals found in cannabis flowers. The molecule acts as an aromatic terpene, contributing pleasant notes of spice, pepper, and wood. Moreover, as a dietary cannabinoid, it interacts with the human endocannabinoid system, affecting a wide range of physiological processes. Early research suggests that the compound synergises with CBD and that it could play a future therapeutic role in areas such as drug addiction, liver disease, and chronic pain. Hopefully, as the research barriers surrounding cannabis start to fall, we’ll see more studies that shine a light on the complex entourage effect surrounding beta-caryophyllene, cannabinoids, and other terpenes.
- Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid https://www.pnas.org
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol and Beta-Caryophyllene https://www.mdpi.com
- Cannabis sativa Induce Antinociception in Mouse Chronic Neuropathic Pain https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Global incidence and prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - PMC https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Beta-Caryophyllene Modifies Intracellular Lipid Composition https://iris.unito.it
- Effects of β -caryophyllene, A Dietary Cannabinoid https://www.ingentaconnect.com


























































