.

Phytoremediation: Can Cannabis Clean Our Contaminated Soils?
Soil is crucial to life. It contains everything required to grow healthy food, which we need to build healthy bodies. However, we've abused agricultural soils, and now countless acres are contaminated with substances such as heavy metals, pesticides, and even radioactive material. Thankfully, cannabis could help us get out of this mess.
Contents:
- What is phytoremediation?
- The role of cannabis in phytoremediation
- Properties that make cannabis a good phytoremediator
- Which contaminants can cannabis clean up?
- Can cannabis used for phytoremediation be smoked or consumed?
- Challenges and limitations of cannabis phytoremediation
- The future of cannabis phytoremediation
- Cannabis phytoremediation: a promising strategy for cleaner soils
Key Points
- Phytoremediation uses plants to clean up pollutants in the soil.
- Cannabis shows potential as a phytoremediator, effectively accumulating heavy metals, pesticides, and radioactive substances.
- Several countries have already started using cannabis for phytoremediation.
- Scientists will likely find more effective ways to clean soils with cannabis, including the application of symbiotic microbes.
Our soils are under strain. Decades of misuse and pollution have decimated areas of arable land, essentially leaving them poisoned. However, cannabis could hold the key to cleaning them up and restoring them to a healthy equilibrium. Find out how below.


What Is Phytoremediation?
The Greek “phyto” means plant, whereas “remediation” comes from the Latin “remedium”, which means “restoring balance”. Put these two puzzle pieces together, and we have ourselves a handy plant-based technology.
Phytoremediation involves growing specific plants in soils contaminated with heavy metals, pesticides, and other toxic substances. These plants are able to accumulate pollutants, removing them through the soil by pulling them up through their roots. These plants are then harvested and processed, preventing pollutants from re-entering the soil. Likewise, some plants stimulate microbes in the soil that help to break down contaminants, rendering them less harmful.
Ultimately, phytoremediation "cleans" soils in a natural and sustainable way. It helps to heal misused land, restoring its agricultural potential and making it safer for humans and wildlife.
-
The Importance of Phytoremediation
So, why the hype around phytoremediation? Unfortunately, it’s because we’re facing a very big problem.
Reports show that soil contamination is affecting the quality[1] of agriculture, creating a yield loss of 15–20%. Degradation of land and soil currently affects 3.2 billion people[2] (40% of the world’s population).
In Europe, 80% of agricultural soils contain pesticide residues in the form of glyphosate, DDT, and other chemicals. These chemicals translocate up the food chain; research has detected glyphosate in 99.8%[3] of urine samples gathered in France.
Both heavy metals and microplastics also pose significant challenges to soil health. In the UK, an estimated 22,500 tonnes[4] of microplastics are released into the soil each year through fertilisers and additives, machinery, and wind dispersion.
Though these figures paint a dire picture of the impact of humans on the environment, they’re essential in identifying urgent solutions. There are a variety of known ways to remediate soils, including physical methods such as excavation, chemical methods including oxidation, and thermal methods involving incineration.
However, phytoremediation offers certain benefits that the alternatives lack. Plants are an environmentally friendly and aesthetically pleasing option that generate less secondary waste. Phytoremediation creates fewer environmental disturbances than the alternatives, preserves soil health, and can help capture atmospheric carbon dioxide.
However, using plants also has some drawbacks. As a part of the ecosystem, plants could introduce contaminants into the food chain. Individual plants also have limited root zones, and they’re often slower to remove contaminants compared to conventional methods.
-
The Science Behind How Plants and Fungi Clean Soil
Plants aren’t alone in their capacity to combat soil contamination. Fungi, belonging to an entirely distinct kingdom of life, also show promise for cleaning up environmental toxins. Both of these organisms achieve this through the following mechanisms.
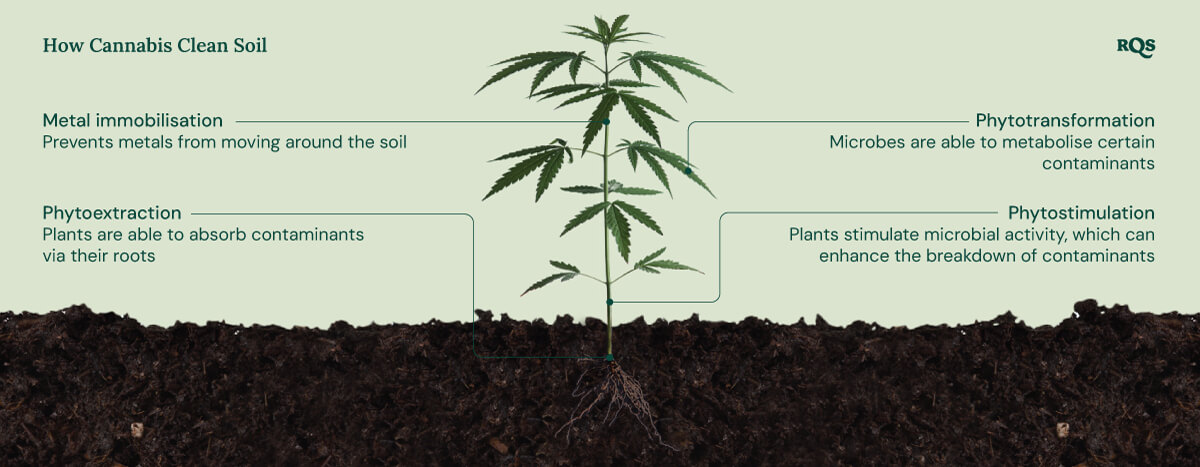
- Phytoextraction: Just as they take up nutrients, many plants are able to absorb contaminants via their roots, while fungi do so via tiny root-like threads called hyphae.
- Phytostimulation: By releasing exudates into the root zone, plants and fungi stimulate microbial activity, which can enhance the breakdown of contaminants.
- Phytotransformation: Plants, fungi, and microbes are able to metabolise certain contaminants, transforming them into less-harmful substances.
- Metal immobilisation: Some fungal species are able to bind metals to their surfaces through glomalin production, preventing them from moving around in the soil.

The Role of Cannabis in Phytoremediation
Cannabis shows great potential in the field of remediation. While cannabis plants grown for consumption must be cultivated in high-quality substrates and under tightly controlled conditions, industrial hemp possesses several characteristics that make it a good candidate for removing contaminants from soils, including heavy metals, pesticides, and organic substances.
Already, hemp has proven its worth in the field. So far, data shows that hemp has the capacity to pull heavy metals[5] such as tungsten and arsenic out of the soil. Likewise, the plant also has the potential to clean up pesticides, solvents, and petroleum-based compounds.
Properties That Make Cannabis a Good Phytoremediator
Hemp possesses several key traits that make it an attractive candidate for phytoremediation projects. These properties include:
- Deep roots: Hemp plants produce extensive root systems that can reach depths of 3 metres. They can access more soil volume than other plants, and therefore have the ability to capture more contaminants.
- Rapid growth: Hemp plants can reach a height of 400 cm in just 100 days. This quick growing cycle allows for relatively quick cleansing of soils.
- Significant biomass: The large root systems and substantial aerial parts of hemp plants culminate in plenty of biomass, allowing them to store substantial quantities of contaminants.
- Adaptability: Hemp plants are hardy and tolerate a range of conditions, from cold and rainy climates to dry and arid.
- Metal tolerance: Hemp plants are able to absorb and store heavy metals without showing signs of toxicity.
-
How Does Cannabis Compare to Other Plants?
Cannabis offers advantages both during and after phytoremediation. Research shows that hemp outperforms Indian mustard[6] when it comes to cleaning up heavy metals such as molybdenum, vanadium, and tungsten.
Hemp also grows much faster than tree species used in phytoremediation, such as poplar and willow. On top of its effectiveness in the field, hemp also offers distinct economic benefits that make it an attractive option.
-
Economic Benefits of Using Hemp
Humans have used hemp since antiquity to make rope, clothing, paper, canvas, and many other products. While contaminated cannabis plants certainly have no place in the consumer market, they still have potential applications.
- Biofuel: Contaminated hemp plants can be processed into biofuels, such as bioethanol and biodiesel.
- Construction: Hemp fibres can be used to create hempcrete or insulation, where contaminants are bound up in a solid matrix.
- Phytomining: This process extracts heavy metals from contaminated plants, which have uses elsewhere in industry. For example, copper is a valuable material for electrical wiring and motor coils.
Which Contaminants Can Cannabis Clean Up?
Hemp shows promise at cleaning up some of the most persistent and noxious contaminants that human agriculture and industry have introduced into the soil. Various studies have proven the plant's effectiveness against some of the contaminants below, while its innate traits suggest its efficacy against several others.
- Heavy Metals
- A review[7] published in the journal Plants reports on the effectiveness of cannabis in removing heavy metals from the soil. These substances cause all kinds of problems in agricultural environments, from ecosystem disruption and food chain contamination to groundwater pollution and plant toxicity. Research shows that hemp plants can help to remove this burden, particularly concerning levels of lead, cadmium, and arsenic.
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)
- PAHs are organic pollutants formed during the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, wood, and organic matter. These substances are known to harm soil biology, including beneficial bacteria that are important for nutrient cycling and overall soil health. Cannabis shows promise[8] in removing PAHs such as benzo(a)pyrene and chrysene from affected soils.
- Organic Contaminants
- Organic contaminants include a range of pesticides, herbicides, and industrial solvents that linger in soil where they disrupt soil microbes. Runoff into groundwater also poses a risk to both animals and humans. Field studies conducted in Hawaii show that industrial hemp can speed up the degradation of atrazine—a herbicide linked to cancer[9], reproductive problems, and damage to wildlife.
- Oxyanions
- These negatively charged molecules mostly originate from agricultural fertilisers and mining operations. Left unchecked, they leach into groundwater and pose a risk to human health and aquatic ecosystems. Studies[10] have shown that cannabis has the ability to draw oxyanions such as arsenate and molybdate up from the soil.
- Radionuclide
- Radioactive elements, such as uranium, caesium, and strontium, contaminate the environment following nuclear accidents and mining activities. They pose significant health risks and a long-lasting environmental impact due to their extended half-lives and radiotoxicity. Early research[11] suggests that hemp could help to reduce radionuclide soil toxicity.
-
Real-World Applications
While the application of cannabis for phytoremediation is still a rarity, there are a few real-world examples that demonstrate the plant’s effectiveness.
- Ukraine: Researchers planted hemp[12] around Chernobyl following the famous nuclear disaster and found it to reduce radioactive contamination in the soil.
- Italy: Cannabis plants are currently being used to clean up[13] agricultural land contaminated with dioxin from a steel plant in Italy.
- Lithuania: Citizens are currently allowed to grow hemp plants on private property for the purpose of phytoremediation.


Can Cannabis Used for Phytoremediation Be Smoked or Consumed?
No. Cannabis grown on contaminated soil poses a danger to users. Because these plants accumulate heavy metals, organic compounds, radioactive components, and other dangerous substances, they are not suitable for consumption. Regulatory testing in countries and states with legal weed industries helps to keep consumers safe from cannabis grown in such environments.
-
Safety Concerns of Contaminated Cannabis
Because cannabis has such a tendency to accumulate contaminants, growers must ensure they’re growing plants in suitable soil. An initial soil test can help to rule out any contamination, while adopting organic practices can help to keep the soil healthy and clean going forwards.
The short-term symptoms of using contaminated cannabis include nausea, headaches, respiratory issues, and dizziness. Long-term effects include serious health conditions such as cancer, neurological problems, and heart issues.


Challenges and Limitations of Cannabis Phytoremediation
Cannabis certainly shows great promise when it comes to cleaning up our soils. However, some barriers exist that have stunted its application in soil remediation.
-
Barriers to Widespread Adoption
The primary barriers to the widespread adoption of cannabis for soil remediation include:
- Legal restrictions: While many countries have legalized the cultivation of hemp, it remains illegal in certain countries.
- Quicker alternatives: Although less environmentally friendly, governments and businesses are more likely to opt for techniques such as excavation and incineration for faster results.
- Biomass disposal: The proper disposal of contaminated plant material remains challenging, and infrastructure needs to catch up before widespread adoption is feasible.
-
Research Gaps in Phytoremediation
Research surrounding cannabis phytoremediation still remains early. As such, scientists are now working to optimise its application by considering the following:
- Standardisation: Testing different hemp cultivars on different contaminants and soil types will help to standardise phytoremediation strategies.
- Long-term effects: Researchers need to identify the long-term environmental impact of cannabis cultivation, especially regarding the impact of contaminated plants.
- Optimised techniques: Advances in soil science continue to elucidate the symbiosis between crops and microbes. Scientists will likely invest time and energy into testing different inputs in hemp plants to see how they impact phytoremediation.


The Future of Cannabis Phytoremediation
While hemp phytoremediation is uncommon at present, the future certainly looks bright. Cannabis has already shown great potential for cleaning our soils, and the demand for the plant will only increase as our environmental situation sadly worsens. Let’s take a look at what the future could hold .
-
Advances in Genetic Engineering
Cannabis has innate properties that make it a good phytoremediator. However, researchers are considering bioengineering the plant to make it even more effective. This technology will help scientists breed hemp plants with an improved ability to uptake and accumulate heavy metals. Genetic engineering could also produce plants that offer higher levels of biomass and target specific pollutants.
-
Economic and Environmental Opportunities
Cannabis phytoremediation could also bulk up the economy in many countries while also supporting environmentally friendly initiatives. Government subsidies could reward farmers for planting hemp for this purpose, and new job opportunities could emerge to meet the demands of processing harvested plant material.
Cannabis Phytoremediation: A Promising Strategy for Cleaner Soils
The misuse of soils through agriculture, and their pollution through industrial activities, poses serious problems for both food production and the wider environment. As the state of our soils becomes more dire, governments are likely to start taking action to tackle the presence of heavy metals, organic compounds, and other pollutants.
Alongside physical and chemical approaches, cannabis offers an environmentally friendly option. Not only has the plant shown potential in removing pollutants, but it provides an economically valuable product at the end of the process. While the research remains early, hemp will likely play an important role in the future of nature regeneration.
- 80% of world's soils show pesticide residues, FAO says https://resoilfoundation.org
- Soil pollution a risk to our health and food security https://www.unep.org
- Environmental Science and Pollution Research https://link.springer.com
- Agricultural fertilisers contribute substantially to microplastic concentrations in UK soils https://www.rothamsted.ac.uk
- PHYTOREMEDIATION WITH HEMP https://api.mountainscholar.org
- HEMP’S POTENTIAL FOR ENVIRONMENTAL CLEANUP AND ECONOMIC RECOVERY https://api.mountainscholar.org
- Potential of Industrial Hemp for Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals - PMC https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Remediation of Benzo[a]pyrene and Chrysene-Contaminated Soil https://www.tandfonline.com
- Atrazine and Cancer Incidence Among Pesticide Applicators in the Agricultural Health Study (1994–2007) - PMC https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- https://api.mountainscholar.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/d3db73cd-09aa-449d-a29a-3b2333b58198/content
- ERROR 403 - Forbidden! https://www.fundacion-canna.es
- ERROR 403 - Forbidden! https://www.fundacion-canna.es
- Exploring the Potential of Industrial Hemp in Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals https://www.nrfhh.com








































