.

What’s The Difference Between Hemp Seed Oil And CBD Oil?
Cannabis culture has grown exponentially to encompass a whole new circle of hemp users that never get high. Hemp seed oil and CBD oil have become synonymous with health and well-being. By the time you finish this blog, you’ll be better informed about hemp, CBD oil, and hemp seed oil.
Contents:
WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CANNABIS AND HEMP?
First, we need to make it clear that although cannabis and hemp might technically be the same species, they are very different plants to grow. Exclusively female cannabis plants are cultivated by ordinary decent home growers. Our prime directive is to harvest the most psychoactive flowers possible. Photoperiod strains will not bloom without 12 hours of darkness, while autoflowering varieties will begin to bloom around 30 days post-germination.
Feminised seeds, which guarantee 99.9% female crops, are more popular than organic regular seeds as no male plants must be removed. Intersex plants are semi-rare, but stress can turn a female into a “hermie”, with both buds and pollen sacs developing. Cannabis cultivators will cull these plants like males to prevent pollination. Sinsemilla or seed-free flower is the benchmark for high-grade bud.
In contrast, hemp or industrial hemp in the EU contains less than 0.2% THC and less than 0.3% THC in the US and Canada. In fact, the European Industrial Hemp Association (EIHA) has called for harmonisation in the interest of fair competition.
LOW THC! WHAT KIND OF HEMP ARE THEY BREEDING?
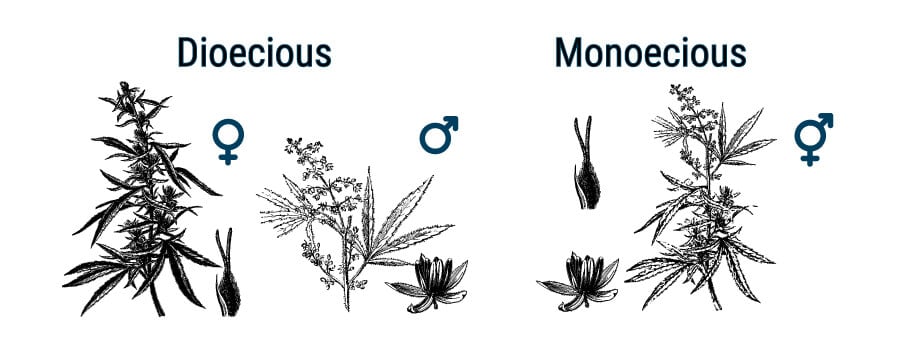
Both dioecious and monoecious hemp varieties are commonly cultivated for fibre, grain, CBD oil, and hemp seed oil by farmers. Moreover, farmers usually grow for dual-purposes, so little goes to waste. There are no feminised hemp seeds of any strain currently available; rather, some female dominant varieties with 65–85% female populations.
Monoecious hemp strains are actually intersex plants. To hemp breeders, this is a desirable trait to increase seed production for hemp seed oil extraction. Furthermore, autoflowering hemp varieties are also popular with farmers as they are not too tall for the combine harvester. Most photoperiod hemp is vegged for 150 days or less, and then harvested before flowering starts. Some of these hemp strains can stretch well above 3m tall and thrive in cooler northern climates.
WHAT IS HEMP SEED OIL?
On average, hemp seed contains around 30% oil by weight. The precious oil rich in essential fatty acids is extracted by cold pressing. This method is not unique to hemp seed oil and similar to extracting black onion seed oil. Cold pressing requires the seeds to be de-shelled; the outer husk must be removed. Then, after some scientific chilling and squeezing, hemp seed oil is extracted.
The oil is unrefined, green-coloured, and all nutritious content is preserved by the cold press process. Seed shattering is a problem for the industry and coupled with the variation in hemp seed size and oil content. Only commercial production is viable.
Few varieties of industrial hemp, like the autoflowering Finnish hemp strain Finola, can produce 2 ton per hectare (ha) yields of seeds. In contrast, Cannabis indica strains are capable of producing in the region of 10–14 tons per hectare. Regardless of whether it’s pressed from cannabis seeds or hemp seeds, the hemp seed oil derived is not psychoactive and contains no THC.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF HEMP SEED OIL?
Hemp seed oil is rich in omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. In fact, it’s the only edible oil that contains greater than 80% polyunsaturated essential fatty acids. Linoleic acid (LA) and linolenic acid (LNA) are found in a ratio of 3:1, which is widely believed by nutritionists to be the optimal ratio.
Another benefit of hemp seed oil is the high levels of vitamin E. On average, 100g of hemp seed oil contains 100–150mg of vitamin E. In case you didn’t know, this vitamin is known for its antioxidant properties. The cosmetic industry can’t stop raving about the anti-ageing properties of this natural nutrient common to cannabis and hemp. Furthermore, it’s pretty common for people to create their own CBD tinctures with hemp seed oil. But hemp seed oil alone does not contain CBD or any other cannabinoids.

WHAT IS CBD OIL?
CBD oil can be extracted from cannabis or hemp. While most recreational, high-THC strains typically contain less than 1% CBD, many legal hemp strains contain 2–3%. CBD-rich cannabis strains have made it possible for home growers to become self-sufficient in generating high-CBD, low-THC flowers.
However, hemp remains the primary source for commercial CBD oil, mostly for legal reasons. 20%+ CBD, seed-free cannabis buds will almost certainly replace CBD oil derived from hemp in the future. In order to achieve the highest yields and purity, most hemp CBD oil manufacturers utilise advanced supercritical CO₂ extraction processes.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF CBD OIL?
CBD interacts with the human endocannabinoid system (ECS) and has many health benefits, from proven anti-inflammatory properties to potential cancer treatments. CBD oil will not get you high because it does not contain THC or any other psychoactive compounds. Supplementing with CBD oil improves homeostasis and can be accurately dosed with a couple of drops under the tongue.

WHERE IS ALL THIS LEGAL HEMP COMING FROM?
Only since the passing of 2014 Farm Bill have some US universities been legally permitted to cultivate hemp for research and development. At present, the US must import hemp seed oil and CBD oil to meet consumer demand.
Meanwhile, in the EU, the industry has grown significantly since the 1970s. EU farmers can even obtain a subsidy for hemp cultivation. It might surprise you, but France is hemp country and the world’s number 1 producer.
According to 2016 EIHA data, 17,000ha of hemp is under cultivation in France. That’s more than half the total 33,000ha for Europe. A diminutive sub-4,000ha leaves US hemp cultivation lagging far behind.







































