.
Cannabis Chemistry: All About Alkaloids
Alkaloids are present throughout nature and are responsible for over 60% of plant-based pharmaceuticals. However, the alkaloids found in cannabis aren't well understood. In this article, we examine what we know so far about this intriguing group of chemical compounds.
Contents:
Cannabis plants produce an incredible number of different compounds. More than this, they produce an astonishing number of compounds that can directly interact with the human body. While some of these are quite well-known and understood, others remain relatively obscure. But no longer!
In this article, we’re shining a spotlight on cannabis alkaloids. These diverse compounds are very well-known in other contexts, but not so much when it comes to cannabis. But perhaps there’s more to them than we might imagine. Let’s take a look.
Alkaloids: Another Chemical Family Found in Cannabis
The two most well-known groups of compounds found in cannabis plants are cannabinoids (e.g. THC, CBD, CBN, etc.) and terpenes (e.g. linalool, myrcene, pinene, etc.). The former are chiefly credited for cannabis’ distinct effects, while the latter are largely responsible for the aroma and flavor of the plant, though they are also believed to influence its effects as well.


However, existing alongside these and other compounds are alkaloids. In cannabis, alkaloids aren’t so well discussed, but if you’ve ever taken magic mushrooms, or wondered about how magic mushrooms work, it’s the alkaloids psilocybin and psilocin that cause the high—so alkaloids can do incredible things.
But back to cannabis. In nature, alkaloids are vital to plant (and fungal) survival. They deter predators, aid reproduction, help protect against environmental threats, and more. Regarding our relationship with cannabis, their importance is less understood.
However, there’s every possibility that unlocking the secrets of cannabis alkaloids will have wide-ranging clinical and recreational implications. We may discover that they influence the overall effects of cannabis—i.e. the entourage effect—or might find that some alkaloids exert worthy effects in their own right.
Only with more research will we find out their full potential!
An Overview of Alkaloid Chemistry
Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing compounds produced in plants and fungi. First identified by Carl Meissner in 1819, the word alkaloid (German “alkaloide”) has its roots in both Latin and ancient Greek. The root comes from the Latin “alkali”, and suffix from the Greek “οειδής” (meaning “like”).
They are a chemically diverse group of compounds with no strict classification. That being said, all alkaloids share a carbon skeleton with nitrogen atoms. They can be divided into two subgroups:
- True alkaloids: Nitrogen is part of a heterocyclic ring, making them structurally complex.
- Protoalkaloids: Nitrogen exists outside of the ring structure, exhibiting different chemical behaviour.
Why Does Cannabis Produce Alkaloids?
It’s not known for sure why cannabis plants produce alkaloids. Although, if we look at why other organisms produce them, we can speculate with a high degree of confidence. Cannabis is likely to contain alkaloids for the following reasons:
- Defensive mechanisms: Alkaloids likely protect against herbivores by deterring or poisoning potential threats. They serve as a chemical shield against harmful fungi, bacteria, and viruses.
- Allelopathy: This is a phenomenon to do with competition and growth, whereby certain alkaloids suppress the growth of competing plants in the area, ensuring cannabis thrives in its environment.
- Reproductive support: Alkaloids can attract or repel pollinators, influencing the plant's reproductive success.
- Stress management: They may also help the plant tolerate environmental stressors, such as extreme temperatures, drought, or poor soil conditions.
- Nutrient storage: Alkaloids act as nitrogen reservoirs, allowing the plant to store and utilise this essential nutrient for growth and development.
Other Plants That Produce Alkaloids
As mentioned, alkaloids are by no means unique to cannabis. In fact, they are abundant in the plant and fungal kingdoms. Though they don’t always have positive interactions with the human body, alkaloids are found in many medicinal and psychoactive plants. In fact, not only are they present, but they tend to be the chemicals responsible for a bulk of their effects. Cannabis could almost be seen as unusual for getting people high with compounds that aren’t alkaloids.
Alkaloids account for over 60% of plant-based pharmaceutical drugs, exhibiting diverse biological effects that have made them invaluable in both traditional and modern medicinal, spiritual, and recreational practices.
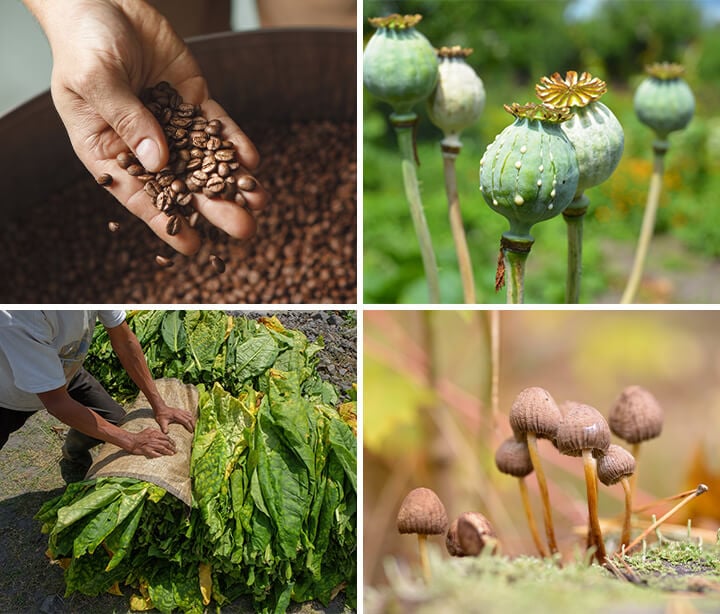
To make it clear how large of an influence alkaloids have on human activity, let’s look at some examples:
- Coffee (caffeine): This is the world’s favorite drug (and alkaloid!), and chances are you’ve consumed some today!
- Poppies (morphine): This alkaloid is a crucial medicine in certain settings and a dangerously addictive drug in others.
- Tobacco (nicotine): A highly addictive stimulant known for its mood-altering effects, it also has an important spiritual role in certain native American cultures.
- Psilocybe mushrooms (psilocybin): Not a plant, but famous enough to be worth mentioning! This is a reality-bending alkaloid which is much-loved by many.


The Potential Benefits of Alkaloids
Given how widely they occur in nature and how many different effects they can have, it’s evident that alkaloids may have many different benefits. Now, we’re not specifically discussing cannabis-derived alkaloids here, but just alkaloids in general.
Here are some of the therapeutic effects some alkaloids are known to exhibit:
- Pain: Some alkaloids can influence pain. Take morphine for instance; this is one of the most commonly used pain-relieving medications, and, despite now having many competitors, still remains popular.
- Inflammation: The alkaloid tetrahydropalmatine is thought to be able to regulate inflammation[1] in certain contexts.
- Antioxidant properties: Tetrahydropalmatine has also been shown to affect oxidation levels in the brains of mice in certain conditions, indicating that it may have some antioxidant properties.
- Mood: There are ongoing studies looking to determine whether psilocybin might be able to affect certain mood disorders such as anxiety and depression. While results are currently inconclusive, the medical community is certainly excited by the possibilities.
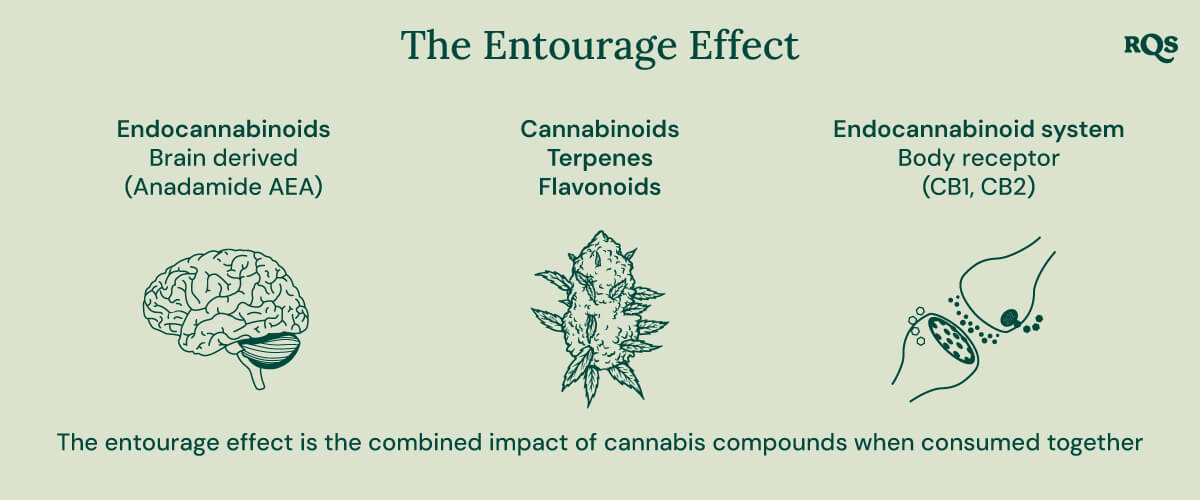
Do Alkaloids Contribute to the Entourage Effect?
There is great interest regarding the entourage effect—the name given to the combined effect of all the active compounds found in any particular cannabis sample working together. Ever wondered why different strains of cannabis have different effects? Well, it’s down to their unique ratios of cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids, and, potentially, alkaloids. While intriguing, we’re a ways off understanding the entourage effect well enough to properly harness it.
But as we discover more about it, many are wondering what, if any, effect alkaloids might have. Well, currently there is no direct evidence linking alkaloids to the entourage effect. But that doesn’t mean they aren’t relevant—it just means we don’t know.
Although speculation here isn’t particularly meaningful, we can imagine that alkaloids in cannabis may indirectly influence cannabinoid activity or interact with relevant receptors, modulating mood, perception, and other effects. These interactions could complement cannabinoids and terpenes, creating a more holistic effect—or not.
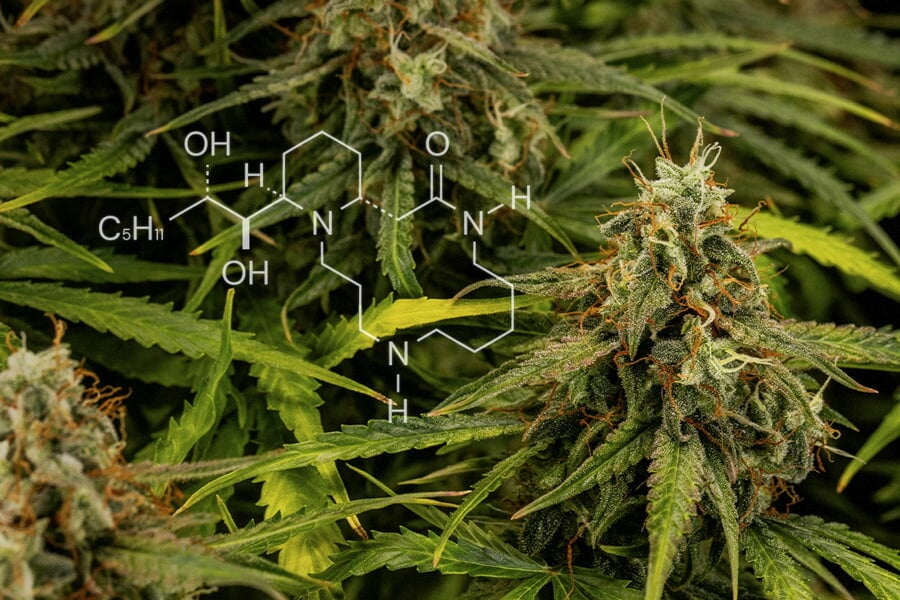
Alkaloids Found in Cannabis Plants
Cannabis is home to a small but intriguing collection of alkaloids. Though overshadowed by cannabinoids and terpenes, these nitrogen-containing compounds are definitely worth investigating more, as some of them may hold currently untapped potential.
Though we can’t look at all of them here, below we’ll explore some of the more notable alkaloids found in cannabis.
- Cannabisativine
- Cannabisativine is one of the first alkaloids identified in the cannabis plant. It is a pyrrolidine-based alkaloid, which means its structure features a five-membered ring containing nitrogen.
A related derivative, anhydrocannabisativine, has also been studied for its slightly altered structure and properties.
It is hypothesised that cannabisativine contributes to the plant's defence mechanisms, offering protection against herbivores or microbial attacks, and its nitrogen content suggests a role in nitrogen storage or recycling within the plant. - Cannabimines (A, B, C, and D)
- The cannabimines are a group of alkaloids classified into four subtypes: cannabimine A, B, C, and D. These are nitrogenous compounds that vary slightly in their molecular structure, resulting in potential differences in biological activity. Cannabimines are notable for their structural novelty, adding to the complexity of cannabis chemistry.
While the precise functions of cannabimines within the cannabis plant are still under investigation, they may play a role in plant defence or stress tolerance. Researchers speculate that they could interact with human receptors or enzymes, opening doors to possible therapeutic applications. - Cannabinine
- Cannabinine (not to be confused with cannabimine) is another alkaloid found in cannabis, distinguished by its nitrogen-containing structure. Its molecular characteristics suggest potential biological activity, though much remains to be understood. As with other cannabis alkaloids, cannabinine’s presence highlights the chemical complexity of the plant.
Early studies suggest that cannabinine may have pharmacological effects, though robust evidence is currently lacking. Its nitrogen-based structure hints at potential interactions with human physiological systems, including neurotransmitter pathways. - Tetanocannabin
- Tetanocannabin is a cannabis alkaloid with a highly distinctive and unique structure. Its nitrogenous framework sets it apart from other known compounds in the plant. The complexity of its structure suggests that it may play an important role in the plant’s adaptation to environmental challenges.
Like other alkaloids, tetanocannabin may contribute to defence mechanisms, helping the plant resist pests, pathogens, or environmental stress. It could also act as a chemical signal within the plant, influencing growth or reproduction.
Tetanocannabin’s pharmacological activity remains largely unexplored, but its structural uniqueness makes it a promising candidate for future drug development studies. Researchers are particularly interested in whether it interacts with human receptors, enzymes, or other systems to produce therapeutic effects.
The Future of Cannabis Alkaloid Research
Discovering more about the alkaloids produced by cannabis plants is a worthy endeavour, whether it’s in the interest of fine-tuning its recreational effects or producing a medical breakthrough.
If nothing else, these compounds go to show just how deep the well of cannabis is. This plant produces an incredible number of different compounds, many of which interact with the human body in notable ways. The ability of cannabis to modulate human beings is very unusual, and can surely be put to good use!
- Potential Therapeutic Applications of Plant-Derived Alkaloids against Inflammatory and Neurodegenerative Diseases https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com





































