.

How Cannabis Interacts With Antidepressants
Cannabis and antidepressants both work to boost happy brain chemicals, and even give rise to the creation of new brain cells. However, using the two together can result in potentially dangerous interactions. Some antidepressants don't mix with cannabis, whereas others could be much more compatible. Find out about these interactions in detail below.
The relationship between cannabis, mental health, and antidepressants.
Contents:
Cannabis and mental health share a controversial—and at times paradoxical—relationship. Some cannabis smokers use the herb to elevate their spirits and boost their mood, and some even need the plant to help them get out of bed in the morning. In others, cannabis can invoke feelings of paranoia and other mood disturbances.
There are conflicting views in healthcare when it comes to cannabis and depression. Some studies hold that certain cannabis compounds may help to take the edge off some symptoms, whereas others suggest cannabis abuse leads to symptoms of depression—or vice versa—and interacts dangerously with conventional medication for the condition.
Continue reading to explore the relationship between cannabis, depression, and antidepressant medication.
Cannabis and Mental Health: A Complicated Relationship
Cannabis affects different people in different ways, especially when it comes to mental health. Most people familiar with the effects of the herb will vouch that it does a reliable job of improving mood. A few tokes on a joint can boost dopamine levels, reduce feelings of nervousness, and soothe the body.
These outcomes help many people across the world deal with certain mental health conditions. However, research also associates cannabis with adverse mental health outcomes. Although no research draws a direct link between consuming cannabis and depression, surveys report a high incidence of depression in heavy cannabis smokers[1] compared to non-smokers.Cannabis may also trigger underlying health mental conditions in some individuals.
The psychotropic effects of the herb can stoke symptoms of schizophrenia and psychosis—serious mental health disorders—in those predisposed to the conditions.
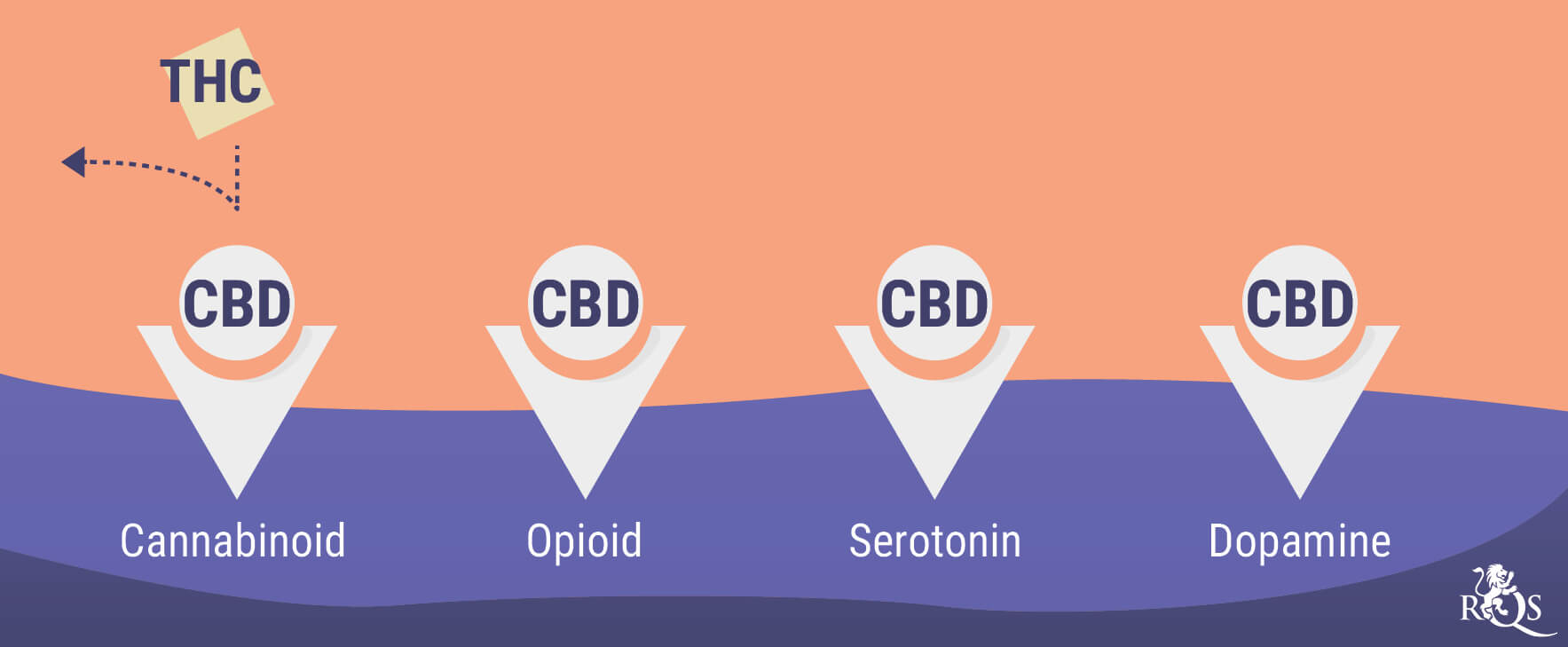
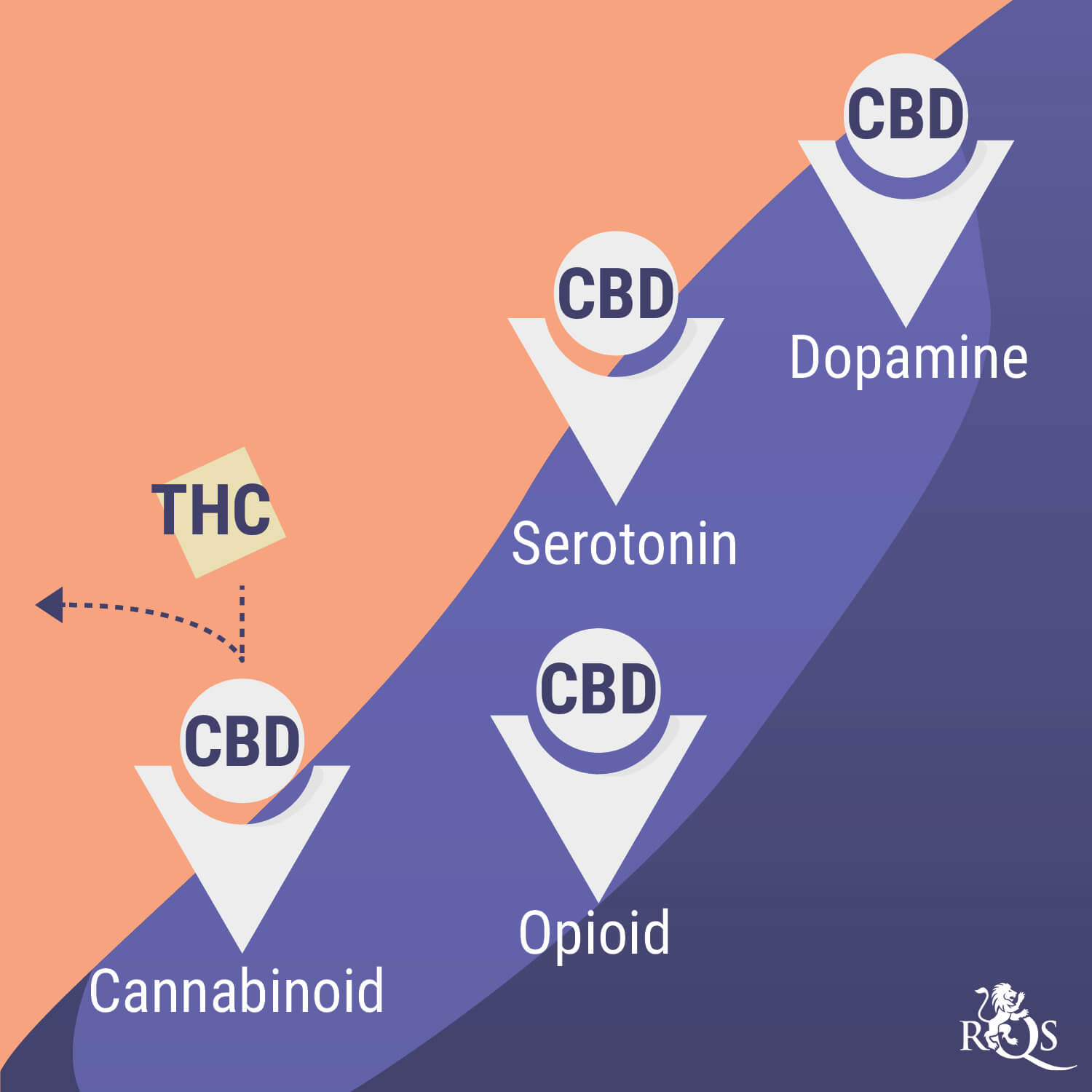
The cannabinoid THC produces the psychotropic effects of cannabis; however, over 100 cannabinoids exist in the plant, and most are non-psychotropic. In fact, molecules such as CBD can help to inhibit some of the effects of THC, and show potential in the field of mental health[2].
Cannabis and Antidepressants
Staggeringly, over 260 million people[3] across the world suffer from depression, and millions take antidepressant medication[4] to manage their symptoms. However, people with depression are more likely to smoke cannabis. Both weed and antidepressants create profound short and long-term changes in the brain, and frequently interact with each other. Before we delve into the safety issues of this combination, let’s explore the unique effects of each drug.
How Does Cannabis Affect the Body?
Cannabis interacts with several major physiological systems. As their names suggest, cannabinoids primarily target the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS plays a fundamental role by regulating many other systems and helping the body maintain biological equilibrium, aka homeostasis.
Among others, the synaptic space between the neurons of the ECS features three main components: receptors, signalling molecules (endocannabinoids), and enzymes that create and break down these molecules. Interestingly, phytocannabinoids such as THC share a similar molecular structure with endocannabinoids, allowing them to bind to the same receptors.
After taking a hit from a joint or bong, THC diffuses through the alveoli in the lungs, enters the bloodstream, and passes into the brain. Here, the molecule binds to CB1 receptors of the endocannabinoid system, where it gives rise to its psychotropic effects—a high.
This binding also boosts dopamine levels and neuronal activity in the brain. Dopamine plays a role in the brain’s reward system and makes us feel pleasure after eating or practising sport.
This surge in feel-good neurotransmitters might help some users feel relief from their depression symptoms, at least for a while. However, with long-term use, THC begins to blunt the dopamine system[5] and may even block the dopamine response to other stimuli that usually release the chemical.
The neurogenesis hypothesis suggests that depression may arise from an alteration in the creation of new neurons in the brain[6]. The rate of neurogenesis may underpin a healthy and happy brain.
Negative events, such as stressful or traumatic experiences, may alter this rate, leading to depression.
Evidence suggests that the endocannabinoid system helps to regulate neurogenesis, and cannabinoids such as THC and CBD may help drive this process[7] in the brain.
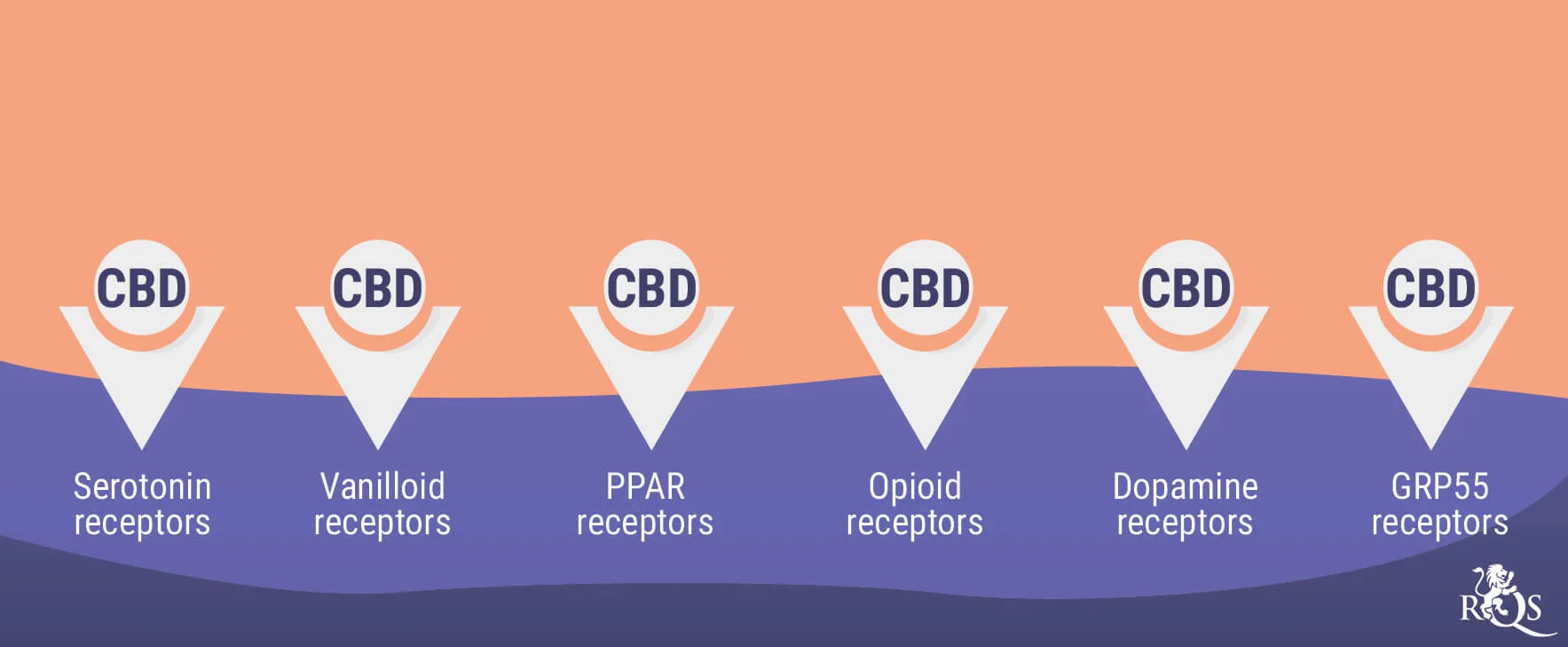
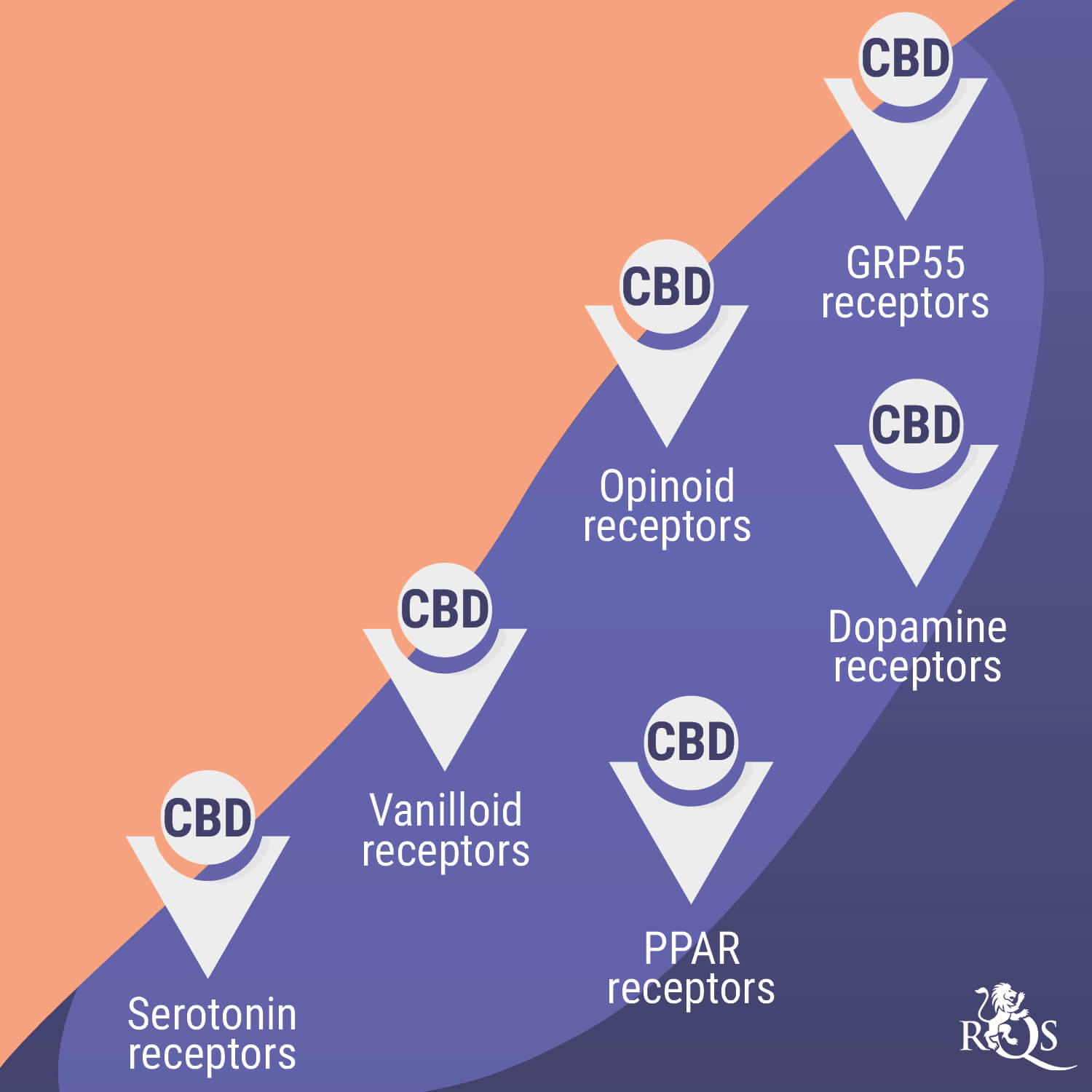
CBD also interacts with numerous bodily systems, including serotonin pathways. As a key regulator of mood and feelings of well-being, serotonin plays an important part in how we feel. The ability of CBD to interface with this system means the cannabinoid may help to take the edge off feelings of nervousness and agitation[8].
How Do Antidepressants Affect the Body?
Antidepressants ultimately aim to improve the symptoms of depression by altering brain chemistry. Although depression has no single cause, a shift in neurochemistry following addiction, emotional life events, or genetic factors may lead to feelings of hopelessness, low mood, and low self-esteem.
Antidepressant medication helps to regulate neurological activity by interacting with systems in the brain that govern mood. Some of these chemicals seek to increase and prolong the presence of brain chemicals, such as serotonin, in the synaptic space. Research also suggests that antidepressants might improve depression symptoms by improving neurogenesis rates within the depressed brain, similar to cannabis.
Interestingly, antidepressants appear to recruit the endocannabinoid system[9], and prolonged use may be involved in long-lasting neuroplastic changes in the brain.
Cannabis' Interaction With Antidepressants
Because both cannabis and antidepressants may provide symptomatic relief, some users might think taking the two together will provide even better results. However, taking cannabis alongside conventional medication can produce dangerous side effects when done incorrectly. Check out the list below to find out which antidepressants interact with cannabis.
Types of Antidepressants
The following drugs may fall into the same "antidepressant" category, but they work in a variety of ways. Varying mechanisms of action mean different drugs interact with cannabis in more or less dangerous ways. Take a dive into the most common antidepressants below and find out if they are safe to take alongside the herb.
-
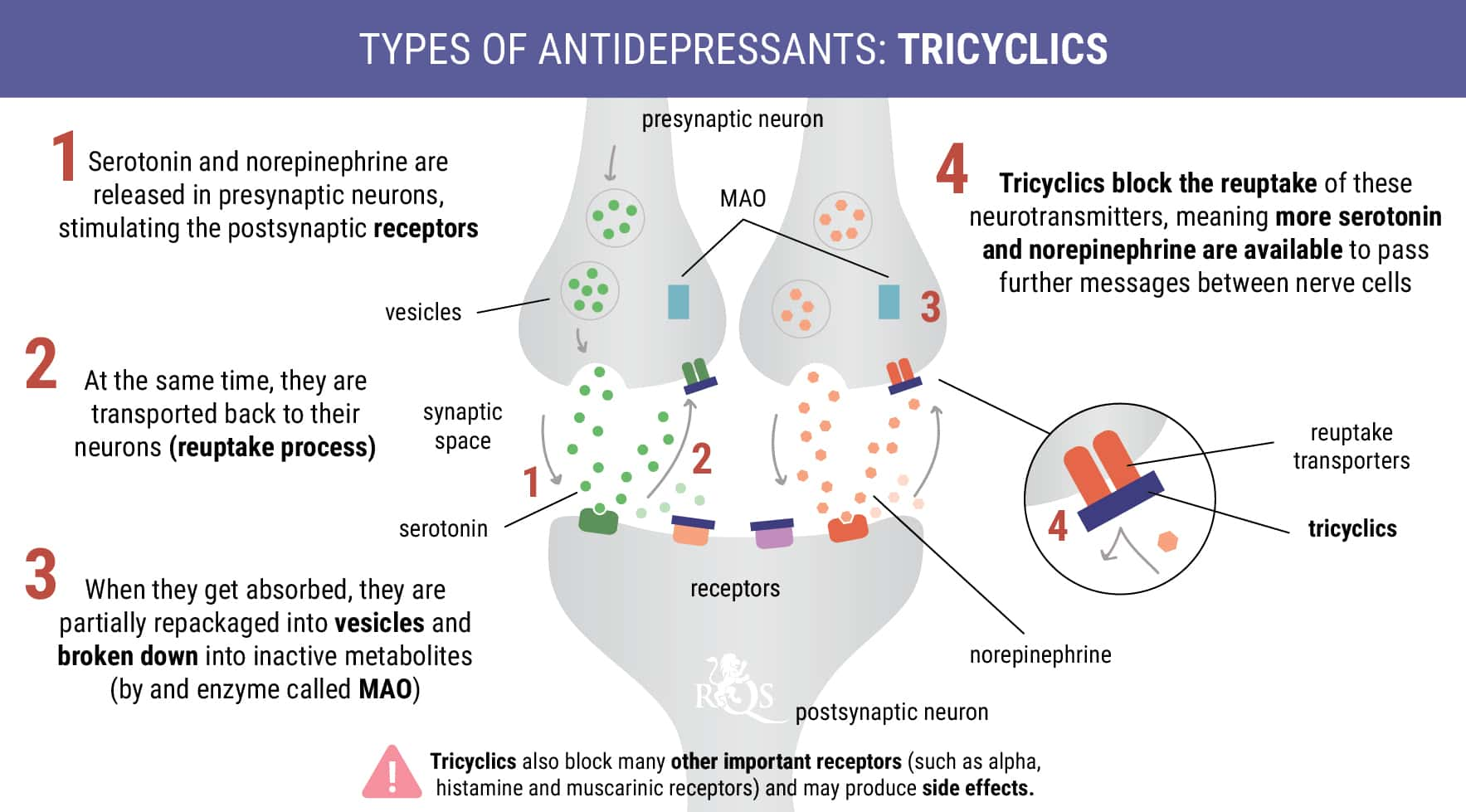
Tricyclics
Tricyclics are among the oldest antidepressants developed. Due to their non-specific mechanism of action, they generally produce more side effects than newer medications. Known by the brand names Tofranil and Surmontil, tricyclics work by changing brain chemistry. These molecules block the reuptake of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and serotonin, ultimately boosting their levels in the brain.
Side Effects
Common side effects of tricyclics include drowsiness, constipation, blurred vision, and a postural blood pressure drop (orthostatic hypotension). Unfortunately, these medications have a high likelihood of negatively interacting with cannabis. Possible side effects of combining the two include potentially life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia-arrhythmia).
-
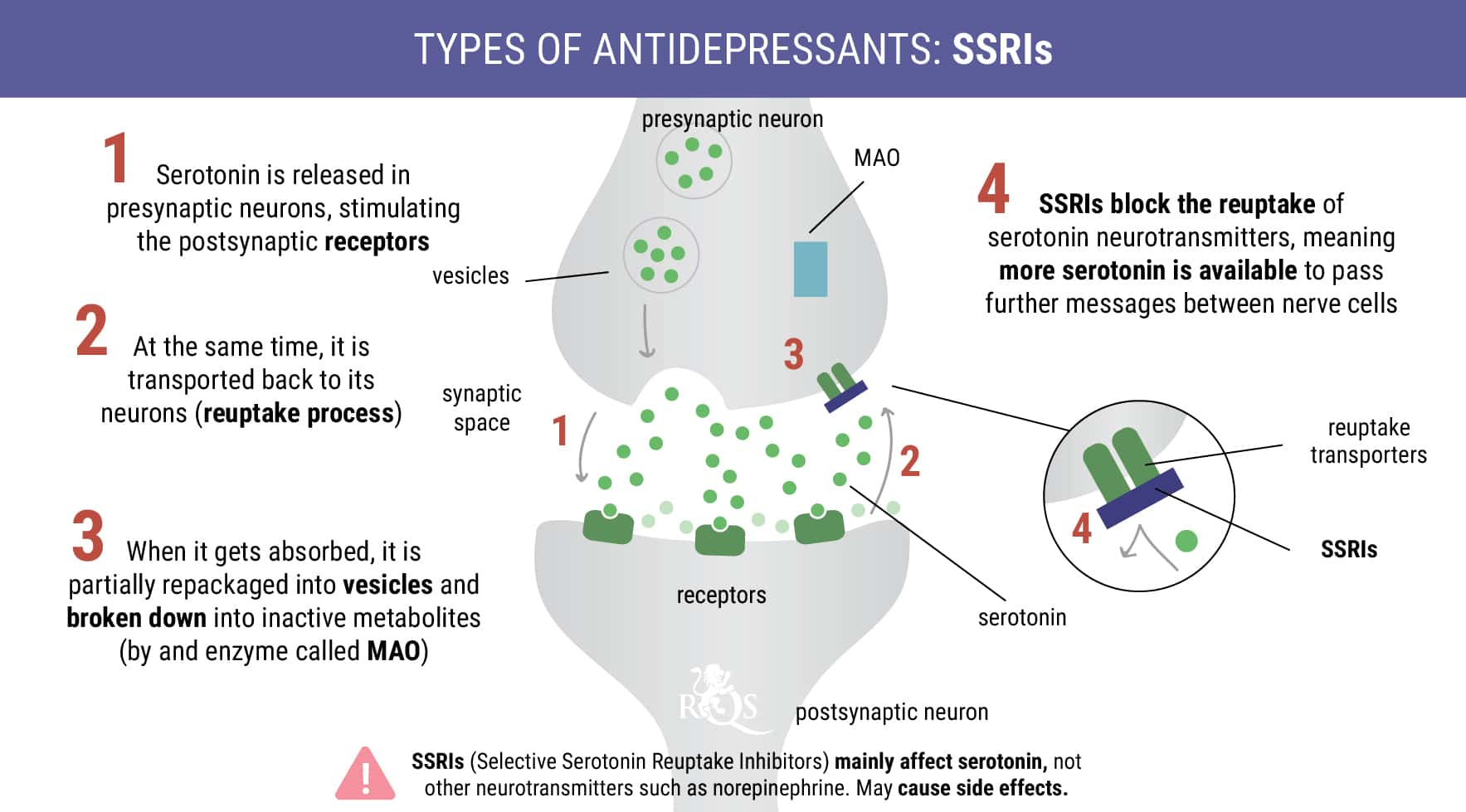
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors include branded drugs such as Prozac. These drugs interact with serotonin receptors in the brain, latching onto these sites in the synapses of neurons and preventing cells from reabsorbing serotonin. High levels of serotonin remain in the synaptic space, where it exerts mood-enhancing effects.
Potential Side Effects
Taken alone, SSRIs can produce side effects such as anxiety, shaking, weight loss, and dizziness. These drugs could also pose a certain risk of negatively interacting with cannabis.
-
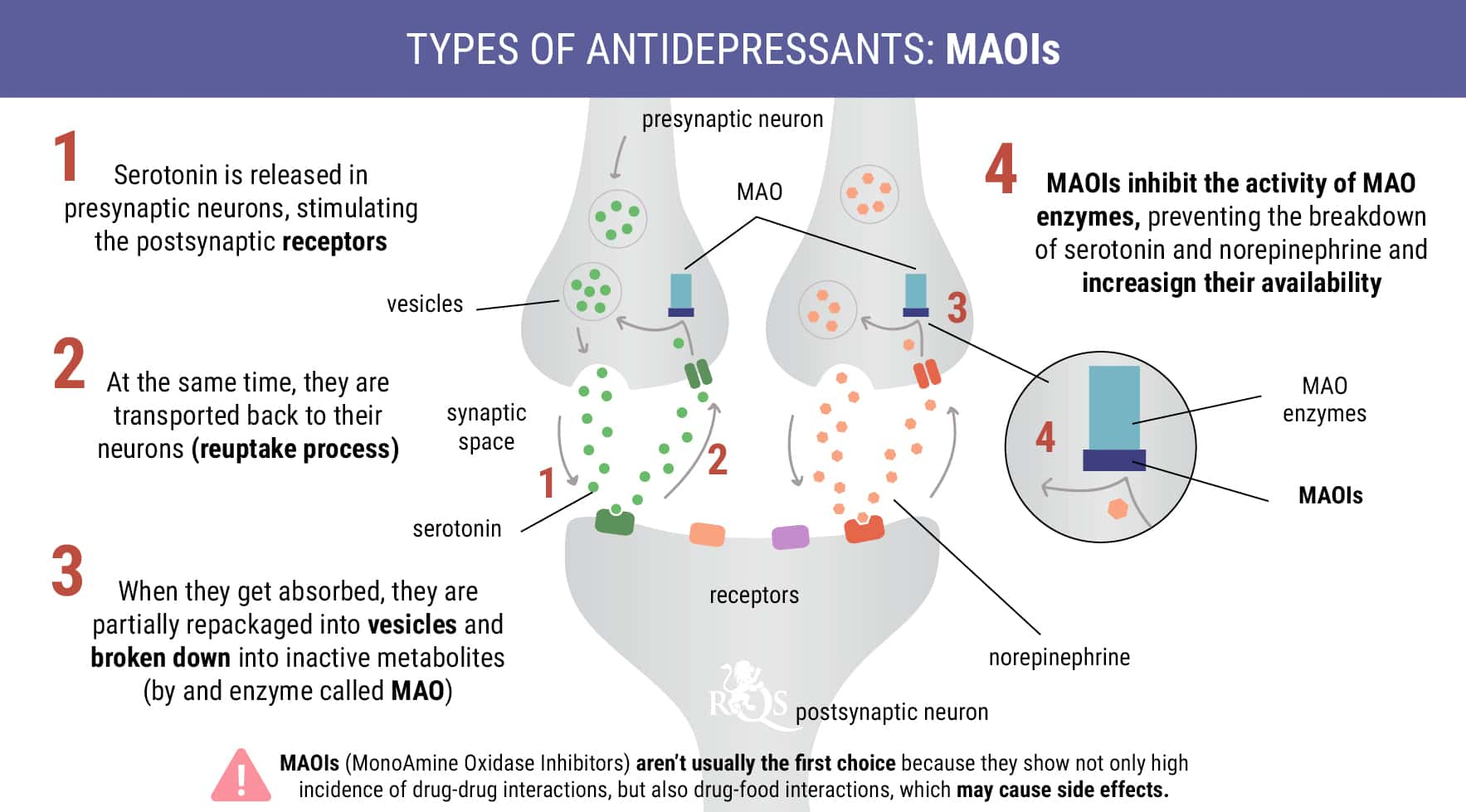
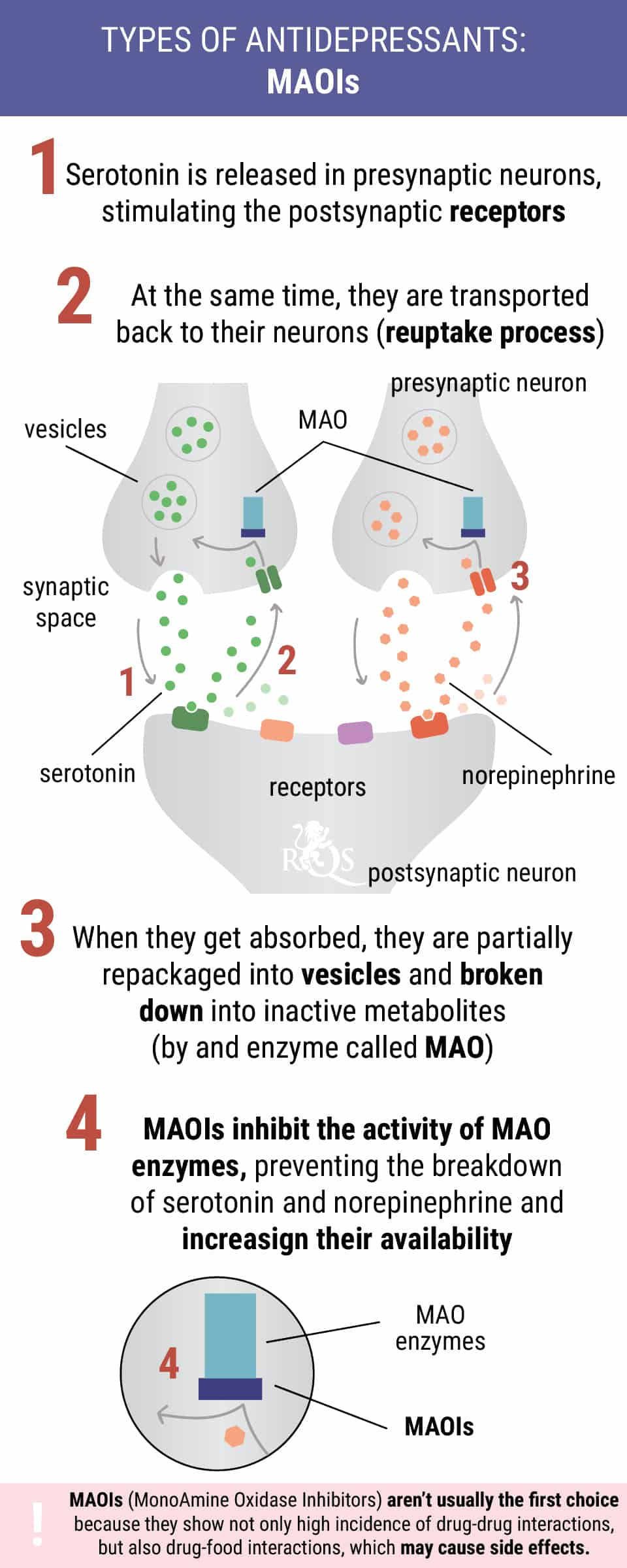
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors work by prolonging the presence of neurotransmitters in the brain. Dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine all fall into the monoamine chemical class. The enzyme monoamine oxidase metabolises and breaks down these molecules. By inhibiting the action of these enzymes, MAOIs lead to enhanced levels of monoamines in the synapses.
Potential Side Effects
MAOIs negatively interact with a long list of foods, including soy, salami, sauerkraut, cheese, and nuts. Common side effects of the medication include fatigue, headaches, insomnia, and reduced or increased libido. MAOIs could interact dangerously with cannabis, and the combination should be avoided
-
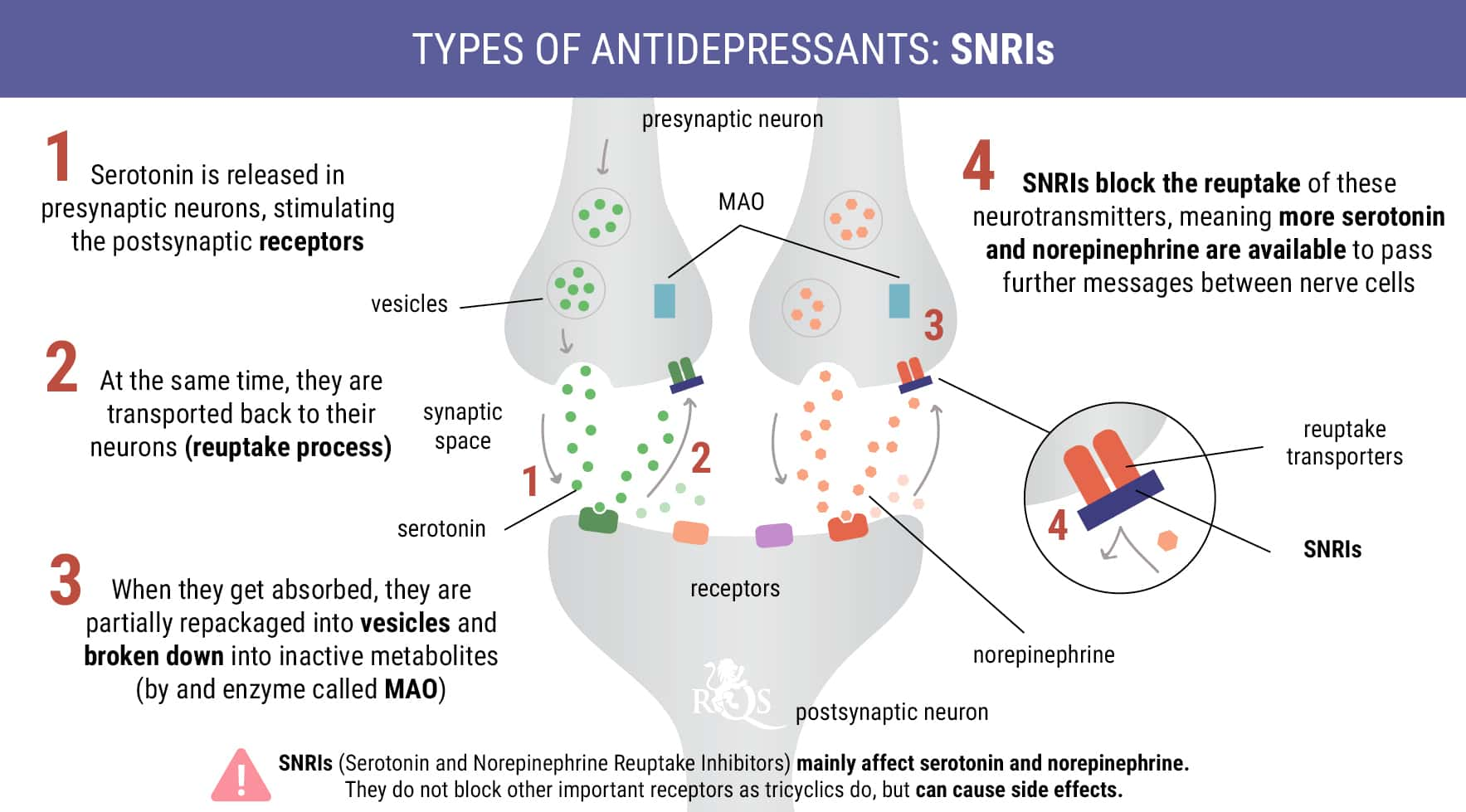
Newer Antidepressants (SNRIs)
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are used to treat symptoms of depression, such as irritability and sadness. Doctors also prescribe these drugs, under the brand names Fetzima and Cymbalta, to treat anxiety disorders and nerve pain. SNRIs work by blocking the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine.
Potential Side Effects
Frequent side effects of SNRIs include dry mouth and excessive sweating. SNRIs are relatively safe for most people; however, they could pose a certain risk of negatively interacting with cannabis.

Risk Factors of Combining Cannabis With Antidepressants
Combining cannabis with antidepressants could pose several risks. The herb may produce the most dangerous outcomes when combined with tricyclics and MAOIs. However, and despite there being no studies availing this, in the case of to smoke, it may be theoretically safer, while taking newer medications such as SSRIs
You should always consult your physician before combining cannabis with any antidepressant to ensure you’re making a safe decision that won’t put your life in danger.
Depending on your personal and family history, among other factors, your risk of having an adverse reaction could be more or less likely.
Does Cannabis Interact With Other Mental Health Medication?
Cannabis may also interact with the common anti-anxiety drug class benzodiazepines (e.g. Xanax). Although no research documents any interaction between the two substances, both work as central nervous system depressants. Moreover, both substances may help to ease feelings of nervousness in some people, while in others may give rise to paranoia and rapid heart rate.
Mixing Xanax and cannabis may result in side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, trouble concentrating, slurred speech, and confusion. Cannabis can also interact with other mental health medication, including sedatives such as Ambien.
What About CBD and Antidepressants
CBD poses a relatively high risk of interacting with antidepressants. Although the cannabinoid doesn't produce psychotropic effects, it does cause shifts in brain chemistry and liver metabolism. CBD can slow down how fast the liver processes antidepressants, causing elevated levels to circulate around the body. Discuss CBD with your doctor before combining it with antidepressants to make sure you do so safely.
Can You Mix Cannabis and Antidepressants?
Some antidepressants could cause dangerous interactions with cannabis; others are could be relatively safe to take at the same time. Ultimately, you should consult a healthcare professional if you wish to use cannabis and antidepressants together. The combination may provide enhanced results in some cases, but you need to ensure you’re being as safe and responsible as possible.
- Marijuana and depression: What's the link? - Mayo Clinic https://www.mayoclinic.org
- The Potential of Cannabidiol as a Treatment for Psychosis and Addiction: Who Benefits Most? A Systematic Review https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Depression https://www.who.int
- Antidepressant consumption in selected countries 2017 | Statista https://www.statista.com
- The effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on the dopamine system https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Depression, Antidepressants, and Neurogenesis: A Critical Reappraisal https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Cannabinoids, Neurogenesis and Antidepressant Drugs: Is there a Link? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Cannabidiol modulates serotonergic transmission and reverses both allodynia and anxiety-like behavior in a model of neuropathic pain https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Cannabinoids, Neurogenesis and Antidepressant Drugs: Is there a Link? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov








































